What is Industry 4.0 in Simple Words

Industry 4.0 is the term used to describe today's industrial revolution, which is the fourth one in history. The advancement of new technologies such as AI, IoT, and cloud computing has revolutionized the way we work and produce.
The Fourth Industrial Revolution
Industry 4.0 is an important term that describes today's industrial revolution, which happens to be the fourth one in history. It's a significant shift in how goods are produced and is reshaping the manufacturing landscape.
The driving force behind Industry 4.0 is the integration of advanced technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud computing.
In Industry 4.0, machines, devices, and systems are getting smarter and more interconnected. They can communicate with each other and make decisions on their own, leading to more efficient and flexible production processes.
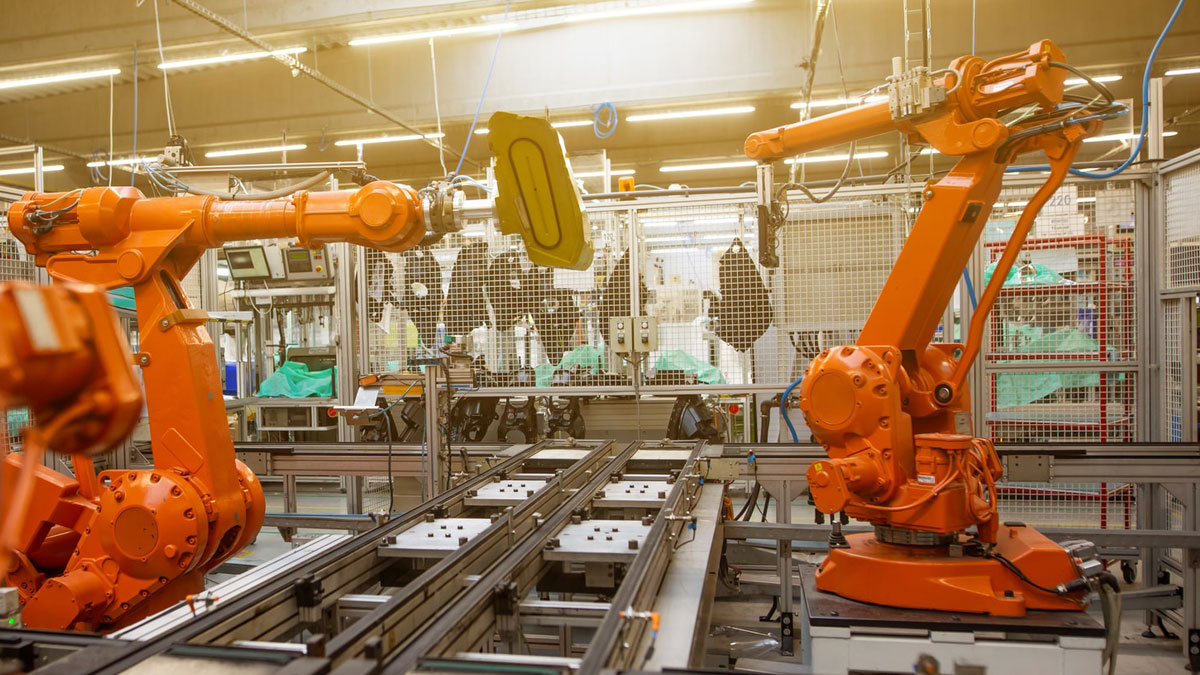

For example, factories are adopting smart systems that optimize operations, predict maintenance needs, and even customize products based on individual customer preferences.
Cloud technologies also have a significant impact on Industry 4.0. They provide a scalable and accessible platform for storing and processing large amounts of data. This allows businesses to leverage analytics and make informed decisions.
"Data is the new oil, fueling the engines of Industry 4.0"
Artificial intelligence plays a crucial role in Industry 4.0. It enables machines to learn from data, make intelligent decisions, and perform tasks without human intervention.
The Internet of Things connects various devices and sensors, allowing real-time data collection and analysis. This connectivity enables seamless coordination and control of different components in the production process.
From Steam Power to AI: Unraveling the Path to Industry 4.0
You know, it's really fascinating when you think about it. To truly grasp the significance of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, we need to look back and delve into the industrial revolutions that paved the way for it.
Each of these revolutions has played a vital role in shaping our world and laying the groundwork for the era of rapid technological advancements we find ourselves in today.
Take the First Industrial Revolution, for example. It occurred way back in the late 18th century and brought about a radical shift in manufacturing. With the introduction of mechanization and steam power, it completely transformed how goods were produced.
We moved away from relying solely on manual labor and embraced machine-based production, which led to a significant increase in productivity and the rise of factories.
Steam-powered factories, Machine tools
Then came the Second Industrial Revolution, also known as the Technological Revolution, in the late 19th century. This was a time of remarkable breakthroughs in electricity, mass production, and the development of transportation infrastructure.
Innovations like the assembly line and the internal combustion engine completely revolutionized industries and fueled economic growth.
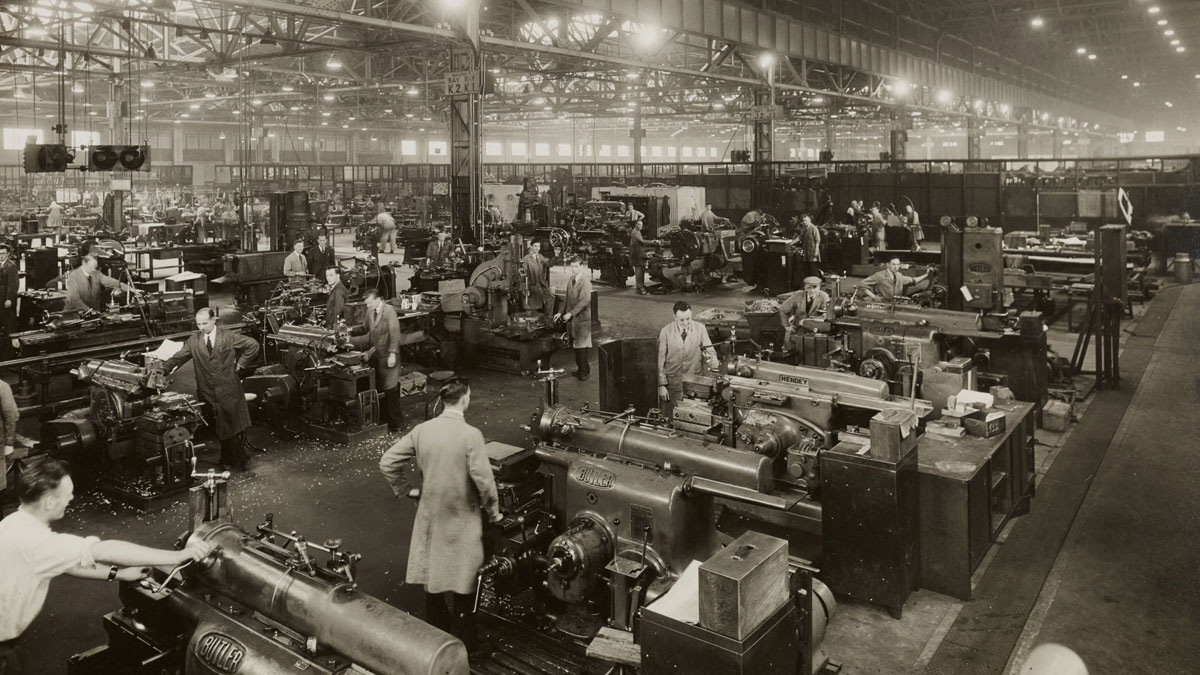

Modern production line, Railroad networks, Telegraph, Electrical power, Telephones
Fast forward to the late 20th century, and we witnessed the emergence of the Third Industrial Revolution, often referred to as the Digital Revolution.
This era was driven by advancements in computing technology, telecommunications, and the widespread adoption of the internet. It completely transformed how we store, process, and share information.
Digitalization and automation became the norm across various sectors, setting the stage for what was to come.

Personal computer, Digital information, The Internet, Cellular phones, Social media
And now, we find ourselves in the Fourth Industrial Revolution, the era we call Industry 4.0. It's marked by the fusion of physical, digital, and biological technologies, resulting in unprecedented levels of connectivity, automation, and data-driven decision-making. The impact of this revolution is immense, reshaping industries and opening up new possibilities.
But you see, to truly understand the significance of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, we must grasp the historical context and progression of the earlier industrial revolutions.
It gives us valuable insights into the patterns of change, the impact of technological breakthroughs, and the societal shifts that have led us to where we are today.
We can see how each revolution built upon the advancements of its predecessors, paving the way for Industry 4.0 and its transformative power.
Essential Topics in Industry 4.0
You know, the Internet of Things, or IoT, is a fascinating concept. It refers to this vast network of interconnected devices and objects. These devices are embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity, which enables them to collect and exchange data.
It's incredible how the IoT is transforming industries and enabling the development of smart systems. It's all about this seamless communication and data exchange between devices, and understanding this is crucial in comprehending Industry 4.0.
And let's not forget about artificial intelligence, or AI, and machine learning. These technologies are at the heart of Industry 4.0. With AI and machine learning, machines and systems can analyze massive amounts of data, learn from it, and make intelligent decisions.
It's like teaching machines to think and learn on their own. And when you grasp the applications of AI, such as predictive analytics and autonomous systems, you start to see the immense potential it holds.
Now, let's talk about cyber-physical systems, or CPS. This is where the physical and digital worlds come together in Industry 4.0. It's about connecting machines, devices, and systems with the internet, creating this seamless integration.
With CPS, real-time communication and coordination become possible, leading to automation, control, and optimization. It's a whole new level of efficiency and interconnectedness.
In Industry 4.0, we can't overlook the significance of big data and analytics. With all the connected devices and sensors, Industry 4.0 generates an enormous amount of data. And to make sense of this data, we need to understand concepts like big data and analytics.
It's about extracting meaningful insights and patterns from this data, empowering us to make informed decisions and drive innovation.
Lastly, there's this emphasis on human-machine collaboration in Industry 4.0. It's about humans and machines working together, leveraging each other's strengths. We're talking about robots and humans collaborating in the workplace, creating safe and efficient environments.
Understanding this collaboration and finding the right balance between human and machine involvement is crucial.
The Impact of Industrial Revolutions on Jobs
Let's explore the impact of each industrial revolution on jobs throughout history. During the First Industrial Revolution in the late 18th century, mechanization and steam power brought about significant changes in the workforce.
While new jobs emerged in factories and industries like textile manufacturing and coal mining, many skilled artisans faced the risk of their livelihoods becoming obsolete. The shift from hand production to machines required workers to adapt to new roles.
Moving on to the Second Industrial Revolution, also known as the Technological Revolution in the late 19th century, we witnessed remarkable advancements in electricity, mass production, and transportation infrastructure. Assembly lines and machinery revolutionized industries.
Although concerns arose about the impact of automation on certain occupations, overall, the Second Industrial Revolution generated more employment opportunities than it displaced, particularly in manufacturing and transportation sectors.
The Digital Revolution, the Third Industrial Revolution, emerged in the late 20th century, bringing advancements in computing technology, telecommunications, and the internet's widespread adoption. It led to the digitization of information, automation of processes, and the rise of knowledge-based industries.
While traditional jobs in sectors like clerical work declined due to automation, new job categories emerged in software development, data analysis, and digital marketing.
Now, we find ourselves in the Fourth Industrial Revolution, commonly referred to as Industry 4.0. It's an ongoing process characterized by the fusion of physical, digital, and biological technologies. Automation, artificial intelligence, and advanced robotics have the potential to transform various industries.
While some job roles may become automated or redundant, Industry 4.0 is expected to create new opportunities in fields like data science, cybersecurity, AI programming, and robotics engineering.
Generative AI: Revolutionizing Industry 4.0 with Infinite Creativity
Imagine this: machines that have the ability to not only learn from data but also generate new and innovative ideas, designs, and solutions. That's what Generative AI is all about. It's like having a creative partner that can assist us in the creative process, taking our ideas to a whole new level.
Let me give you an example that blew my mind. Have you heard of ChatGPT? It's an advanced language model powered by Generative AI. It can understand human language and generate responses that are coherent and contextually relevant.
Imagine having a conversation with ChatGPT, where you can ask it questions, seek advice, or even brainstorm ideas. It's like having a virtual collaborator who can contribute unique perspectives and insights. ChatGPT can generate text in a conversational manner, making interactions feel natural and engaging.
Now, think about how this example of Generative AI can be applied in different industries. From customer service and virtual assistants to content creation, the possibilities are endless. With Generative AI, we have the potential to automate tasks, augment human capabilities, and drive innovation in ways we never thought possible.
Conclusion
Industry 4.0 is today's industrial revolution.
The concept of "industry" is closely tied to employment and the workforce.
Throughout history, the impact on jobs after each industrial revolution has been complex and varied across industries, regions, and time periods.
Adapting to change, continuous learning, upskilling, and embracing new technologies are crucial to navigate the evolving employment landscape in the ongoing transition to the Fourth Industrial Revolution.